REFERENCES TO WORDS AND WORD COMBINATIONS
The references from any specific word give access to the set of words semantically related to the former, or to words, which can form combinations with the former in a text. This is a very important application. Nowadays it is performed with linguistic tools of two different kinds: autonomous on-line dictionaries and built-in dictionaries of synonyms.
Within typical text processors, the synonymy dictionaries are usually called thesauri. Later we will see that this name corresponds poorly to the synonymy dictionaries, since genuine thesauri usually include much more information, for example, references to generic words, i.e., names of superclasses, and to specific words, i.e., names of subclasses.
References to various words or word combinations of a given natural language have the objective to help the author of a text to create more correct, flexible, and idiomatic texts. Indeed, only an insignificant part of all thinkable word combinations are really permitted in a language, so that the knowledge of the permitted and common combinations is a very important part of linguistic competence of any author. For example, a foreigner might want to know all the verbs commonly used with the Spanish noun ayuda, such as prestar or pedir, or with the noun atención, such as dedicar or prestar, in order to avoid combinations like pagar atención, which is a word-by-word translation of the English combination to pay attention. Special language-dependent dictionaries are necessary for this purpose (see, for example, Figure III.2).
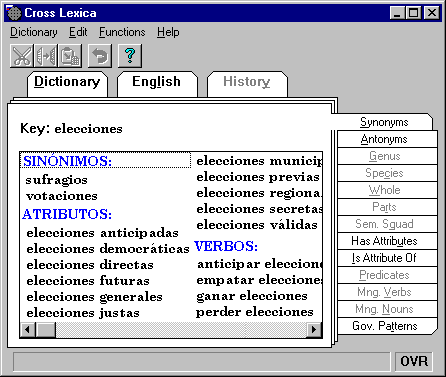 FIGURE III.2. CrossLexica™, a dictionary of word combinations.
FIGURE III.2. CrossLexica™, a dictionary of word combinations.
|
Within such systems, various complex operations are needed, such as automated reduction of the entered words to their dictionary forms, search of relevant words in the corresponding linguistic database, and displaying all of them in a form convenient to a non-linguist user. These operations are versatile and include both morphologic and syntactic issues [37].
Another example of a dictionary that provides a number of semantic relations between different lexemes is EuroWordNet [55], a huge lexical resource reflecting diverse semantic links between lexemes of several European languages.
The ideological basis of EuroWordNet is the English dictionary WordNet [41]. English nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs were divided into synonymy groups, or synsets. Several semantic relations were established between synsets: antonymy (reference to the “opposite” meaning), hyponymy (references to the subclasses), hyperonymy (reference to the superclass), meronymy (references to the parts), holonymy (reference to the whole), etc. Semantic links were established also between synsets of different parts of speech.
The classification hierarchy for nouns is especially well developed within WordNet. The number of hierarchical levels is in average 6 to 7, sometimes reaching 15. The upper levels of the hierarchy form the ontology, i.e., a presupposed scheme of human knowledge.
In essence, EuroWordNet is a transportation of the WordNet hierarchy to several other European languages, in particular to Spanish. The upper levels of ontology were obtained by direct translation from English, while for the other levels, additional lexicographic research turned out to be necessary. In this way, not only links between synsets within any involved language were determined, but also links between synsets of a number of different languages.
The efforts invested to the WordNet and EuroWordNet were tremendous. Approximately 25´000 words were elaborated in several languages.
Дата добавления: 2016-09-06; просмотров: 1844;











