AN REPRESENTATION AND DENOTATION OF SCREW-THREAD ON DRAWINGS
A screw-thread is a surface formed at the spiral moving arbitrary plane a contour on the cylinder, conical or other surface of rotation.
All screw-threads are drawn conventionally on drawings, in accordance with the requirements of State Standard 2.311-68:
on a bolt (external thread): major diameter – by a mainline, minor – by a continuous thin in the distance not less than 0,8mm and no more to the size thread pitch from a thick mainline, on the left side view the minor diameter of screw-thread is shown by an arc, broken in an arbitrary place out of axial lines, length of arcs is ¾ circles;
in an opening (internal thread): minor diameter – by a continuous thick line, major – by a continuous thin line, on a left side view the major diameter of screw-thread is drawn by an arc on ¾ circles, the distance between is the same as for a screw-thread on a bolt .
The limits of screw-thread on the length of a bolt or an opening are drawn by a continuous thick line.
For all screw-threads (except of a pipe and one conical inch) conventional denotations are marked above the size line of major diameter. Pipe screw-threads, cylinder and conical are marked by the lines of foot-notes with pointers and shelves above which the conventional denotation of screw-thread is written. For a conical one inch screw-thread above a shelf the conventional denotation and standards on its basic parameters are written.
A cylinder screw-thread isa screw-thread on a cylinder surface, and conicalon a conical surface. For implementation of screw-thread joints it is necessary to have two parts on one of which a screw-thread is on an external surface (external thread), and on the second – on internal surface (internal thread). A thread formed clockwise and moves along the ax of rotation from an observer is called a right-hand thread. A plane contour that moves anticlockwise along an ax from an observer forms a left-hand thread (LH).
A thread can be formed by spirally moving of one or a few identical plane contours which are located densely near each other along the ax of rotation. In the first case it is a single-start thread, in the second – a multiple-start thread (double-start thread or triple-start thread).
The thread profile is determined by the shape of the cutting tool. They are triangular, square, acme, round and others.
According to their purposes screw-threads can be fastener, motion (translating) (transformation of rotation of motion of one detail on straight line motion) and special.
Let’s consider the basic parameters of screw-thread on the example of metric thread, shown in figure 4.1.
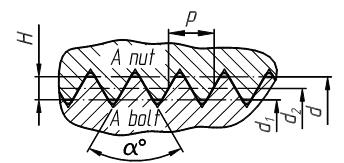
Figure 4.1 - Basic parameters of screw-thread
Parameters of a metric thread: d, d1 - according to major and minor diameters of external and internal -threads, d2 is a middle diameter of a screw-thread, a - a thread angle, Р- a thread pitch, Н- a height. The thread pitch Р is a distance between two neighboring points of thread profile. A lead of thread t– is a distance on which one turn of a screw-thread surface will move along the ax of a screw-thread.
Дата добавления: 2016-07-18; просмотров: 1604;











