Transmitting Information
If you have a sine wave and a transmitter that is transmitting the sine wave into space with an antenna, you have a radio station. The only problem is that the sine wave doesn't contain any information. You need to modulate the wave in some way to encode information on it. There are three common ways to modulate a sine wave:
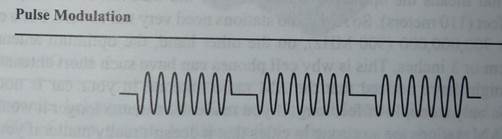
•Pulse Modulation — In PM, you simply turn the sine wave on and off. This is an easy way to send Morse code. PM is not that common, but one good example of it is the radio system that sends signals to radio-controlled clocks United States. One PM transmitter is able to cover the entire United States!
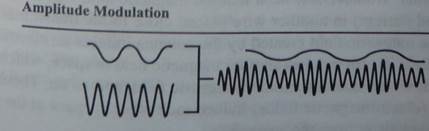
•Amplitude Modulation — Both AM radio stations and the picture part of a TV signal use amplitude modulation to encode information. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the sine wave (its peak-to-peak voltage) changes. So, for example, the sine wave produced by a person's voice is overlaid onto the transmitter's sine wave to vary its amplitude.
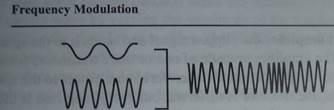
· Frequency Modulation — FM radio stations and hundreds of other wireless technologies (including the sound portion of a TV signal, cordless phones, cell phones, etc.) use frequency modulation. The advantage to FM is that it is largely immune to static. In FM, the transmitter's sine wave frequency changes very slightly based on the information signal.
Onсе you modulate a sine wave with information, you can transmit the information!
Antenna: Real-life Examples
Let’s say that you are trying to build a radio tower for radio station 680 AM. It is transmitting a sine wave with a frequency of 680,000 hertz. In one cycle of the sine the transmitter is going to move electrons in the antenna in one direction, switch and pull them back, switch and push them out and switch and move them back again. In other words, the electrons will change direction four times during one cycle of the since wave. If the transmitter is running at 680,000 hertz, that means that every cycle completes as in (1/680,000) 0.00000147 seconds. One quarter of that is 0.0000003675 seconds. At the speed of light, electrons can travel 0.0684 miles (0.11 km) in 0.0000003675seconds. That means the optimal antenna size for the transmitter at 680,000 hertz is
About 361 feet (110 meters). So AM radio stations need very tall towers. For a cell phone working at 900,000,000 (900 MHz), on the other hand, the optimum antenna size is about 8.3 cm or 3 inches. This is why cell phones can have such short antennas.
You might have noticed that the AM radio antenna in your car is not 300 feet long- it is only a couple of feet long. If you made the antenna longer it would receive better, but AM stations are so strong in cities that it doesn't really matter if your antenna e optimal length.
You might wonder why, when a radio transmitter transmits something, radio waves want to propagate through space away from the antenna at the speed of light. Why can radio waves travel millions of miles? Why doesn't the antenna just have a magnetic field around it, close to the antenna, as you see with a wire attached to a battery? One simple way to think about it is this: When current enters the antenna, it does create a magnetic field around the antenna. We have also seen that the magnetic field will create an electric field (voltage and current) in another wire placed close to the transmitter. It turns out that, in space, the magnetic field created by the antenna induces an electric field in space. This electric field in rum induces another magnetic field in space, which induces another electric field, which induces another magnetic field, and so on. These electric and magnetic fields (electromagnetic fields) induce each other in space at the speed of light, traveling outward away from the antenna.
Bluetooth Basics
Bluetooth is a standard developed by a group of electronics manufacturers mat allows any sort of electronic equipment — from computers and cell phones to keyboards and headphones — to make its own connections, without wires, cables or any direct action from a user. Bluetooth is intended to be a standard that works at two levels:
It provides agreement at the physical level — Bluetooth is a radio-frequency standard.
It also provides agreement at the next level up, where products have to agree on
when bits are sent, how many will be sent at a time and how the parties in a conversation can be sure that the message received is the same as the message sent.

The companies belonging to the Bluetooth Special interest Group, and more than 1,000 of them, want to let Bluetooth's radio communications take the place
of wires for connecting peripherals, telephones and computers.
Дата добавления: 2017-10-04; просмотров: 1756;











