Common cold and runny nose. Can antibiotics cure them?
Antibiotics cannot cure the common cold, one of the most frequent reasons children miss school and adults miss work. Every year, adults have an average of 2–3 colds, and children have even more.More than 200 viruses can cause the common cold, and infections can spread from person to person through the air and close personal contact. Antibiotics do not work against these viruses and do not help you feel better if you have a cold. Rhinovirus is the most common type of virus that causes colds.
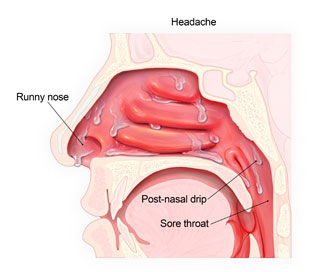
When you have a cold, mucus fills your nose, causing runny nose, congestion, and mucus to drip down your throat (post-nasal drip), which can cause a sore throat and cough.
There are many things that can increase your risk for the common cold, including:exposure to someone with the common cold; age (infants and young children are at higher risk for colds); a weakened immune system or taking drugs that weaken the immune system; season (colds are more common during the fall and winter).
When germs that cause colds first infect the nose and sinuses (air-filled pockets in the face), the nose makes clear mucus. This helps wash the germs from the nose and sinuses. After two or three days, mucus may change to a white, yellow, or green color. This is normal and does not mean you or your child needs antibiotics. Other signs and symptoms of the common cold can include: sneezing; stuffy nose; sore throat; coughing; post-nasal drip (mucus dripping down your throat); watery eyes; mild headache; mild body aches.These symptoms can last for up to 2 weeks.
See a healthcare professional if you or your child has any of the following symptoms: temperature higher than 100.4 °F; symptoms that last more than 10 days; symptoms that are severe or unusual.
If your child is younger than three months of age and has a fever, it’s important to call your healthcare professional right away.
Antibiotics are not needed to treat a cold or runny nose, which almost always gets better on its own. Your healthcare professional will determine what type of illness you or your child has by asking about symptoms and doing a physical examination. Sometimes they will also swab the inside of your nose or mouth. Since the common cold is caused by viruses, antibiotics will not help it get better and may even cause harm in both children and adults. Your healthcare professional can give you tips to help with symptoms like fever and coughing. Rest, over-the-counter medicines and other self-care methods may help you or your child feel better. For more information about symptomatic relief, visit the Symptom Relief section of this website or talk to your healthcare professional, including your pharmacist. Remember, always use over-the-counter products as directed. Many over-the-counter products are not recommended for children of certain ages.
There are steps you can take to help prevent getting a cold, including: practice good hand hygiene; avoid close contact with people who have colds or other upper respiratory infections.
Vitamins
The vitamins are organic substances present in the food of the same order of chemical complexity as the natural hormones. They are not used as a source of energy, but are needed in appropriate usually very small amounts for the carrying out of specific bodily functions and consequently for the maintenance of normal bodily health.
Vitamin A closely related substance is B carotene which is readily transformed in the liver of most animal into molecules of vitamin A. In man carotene is not well absorbed so that in practice the nutritional value of the carotene of the diet is about half that of equivalent amounts of the vitamin.
Results of vitamin A deficiency. Striking changes are found in the eyes, intestine, and respiratory tract the outstanding histological feature is the tendency for stratified epithelia to become greatly thickened and for columnar epithelia to be transformed into transitional or stratified epithelia.
Eyes. The lachrymal glands cease to produce tears. The corneal epithelium becomes thickened, dry and wrinkled and secondarily may undergo necrosis or become infected. Inflammatory processes occur in the conjunctiva and may in vole the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye, leading to complete blindness. The eye disorder is a specific sign of vitamin A deficiency.
Alimentary canal. The cells of the salivary glands do not secrete and appear shrunken: The epithelium of the ducts is proliferated and the lumen is partially occluded. The mucus – secreting cells of the intestine are atrophied and the of the villi are necrotic masses of bacteria may be found filling the Lumina of the glands.
Vitamin B group. This group consists of a series of water soluble organic substances which are found in the tissues of all species from the lowly bacteria protozoa or yeasts up to the highest with tissue oxidations.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid, cevitamic acid). It is found in fresh foodstuffs: fruit juices, e.g., orange or lemon; vegetables, e.g., raw cabbage leaves, tomatoes and to some extent in potatoes. It is present in small amounts in fresh milk (more especially human milk) and in raw meat juice; pasteurized milk is nearly devoid of the vitamin. The vitamin C content of fresh milk varies with the diet of the cow, being large in amount in summer, when the animal is fed on green stiffs, and much less in winter.
Vitamin D promotes calcium and phosphate absorption from the intestine and is essential for the normal calcification of bone and the prevention and cure of rickets. It is found mainly in fish-liver oils and in yolk of egg; it is present to a small degree in animal tats, end is practically absent from vegetable oils (e.g., olive oil). The vitamin D content of milk, butter and eggs depends on the vitamin content of the diet and on the season, being higher in the summer than in the winter.
Vitamin E is found in highest concentration in the embryo of wheat, in olive oil, in seeds and green leaves; there is little in milk fat and none in cod-liver oil. It is present, but not in high concentrations, in animal tissues, chiefly in the fat and muscles.
Vitamin K. Natural vitamin K is a specific fat-soluble dietary constituent of known chemical composition which maintains the normal level of plasma prothrombin and consequently the normal coagulability of blood.
Vitamin K.
Vitamins are substances that your body needs to grow and develop normally. Vitamin K helps your body by making proteins for healthy bones and tissues. It also makes proteins for blood clotting. If you don't have enough vitamin K, you may bleed too much.
Newborns have very little vitamin K. They usually get a shot of vitamin K soon after they are born.
If you take blood thinners, you need to be careful about how much vitamin K you get. You also need to be careful about taking vitamin E supplements. Vitamin E can interfere with how vitamin K works in your body. Ask your health care provider for recommendations about these vitamins.
There are different types of vitamin K. Most people get vitamin K from plants such as green vegetables, and dark berries. Bacteria in your intestines also produce small amounts of another type of vitamin K.
Why do we need vitamin K? Vitamin K is one of the fat-soluble vitamins. It helps the body make proteins that are needed for normal blood clotting. Vitamin K is also needed for making important bone proteins. What happens if we don’t get enough vitamin K? When people don’t get enough vitamin K blood takes a long time to clot. This can cause excessive blood loss and increased risk of death from injuries. Vitamin K deficiency is rare in healthy adults. However, people with severe digestive disorders or on chronic antibiotic therapy may be at risk. Eating very large or very small amounts of vitamin K can change how these drugs work. If you take an anticoagulant, you should pay close attention to your intake of foods such as spinach and turnip greens that are very high in vitamin K, and ensure that your vitamin K intake is about the same from day to day. You should also consult your doctor before taking vitamin E supplements, or supplements such as ginkgo and garlic, as these may also affect blood clotting.
Дата добавления: 2016-09-06; просмотров: 2180;











