Influence of external environmental factors on human health
| № | Environmental factors | Influence on human organism |
| Thermal field, temperature of the environment | Under deviation from optimal temperature (20–22 оС) to the increase or decrease metabolism is changing, organ’s and system’s biorhythms are disrupted and inflammatory and allergic reactions are aggravated. It is believed that thermal regime of the environment influences morphometric and anatomic indicators of the human’s organism. | |
| Atmospheric pressure | Change of atmospheric pressure causes disruption of metabolic processes and can initiate hyper and hypotonic crises, headaches and decrease ability to work and increase intensification of chronic diseases. | |
| Humidity | Excessive humidity facilitates activation of respiratory and inflammatory processes and assists in formation of the centres of epidemic diseases. | |
| Chemical components of the environment | They have a wide range of influence on the human body – from stimulation of some functions of growth and development to suppression and death. | |
| Gravitation | Change of intensity of gravitation (under artificial conditions or, for example, at different Moon phases) influences at least on irritability of nervous system and other functions of the organism. | |
| Magnetic and electromagnetic fields (magnetic storm, local magnetic fields of domestic appliances and so on) | Change of intensity and frequency of vibrations of electromagnetic and magnetic fields cause hypertonic and hypotonic crises, facilitate stenocardia, disrupt heart rhythm, increase the quantity of heart attacks and diseases, increase capillary pressure, change nervous, endocrine and immune system, as well as influence red-ox processes at cellular and sub-cellular level. Other deviations are also possible. | |
| Noise and vibrations | They decrease level of attention, deteriorate general condition, increase the quantity of mistakes, cause stress and oppress central neural system, provoke change of pulse and breath level, disrupt metabolism and facilitate hypertension and heart diseases. | |
| Ionising radiation | It could provoke radiation sickness, malignant tumour, leucosis, and induce intensification of hereditary diseases. Marrow, small intestine and central nervous system are most sensitive to ionising radiation. |
It is a given general principle of the influence of ecological factors on human’s and animal’s organisms that the effect or intensiveness of its influence depends on the nature of the factor itself and on its quantity (for chemical factors) or dose (for physical factors). Those dependencies of the influence of concentration or dose of the certain ecological factor on this or that vital indicator (in the long run it could be the quantity of population) are non monotonous and are generalised on the figure 6.2.


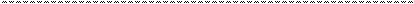

Figure 6.2. Graphic demonstration of generalised dependence of intensive influence of ecological factors (dose, conventional units) on vital indicators of the organism or population (effect, conventional units)
Interrelation between the state of the environment and people’s health has become unique and indisputable. High quality of the environment does not guarantee 100% health of the population but its influence would not become aggravating for the people’s health. At the same time deterioration of the environment resulting from human activity inevitably increases risks for human health. It should be known and remembered, at the least. At the most, people’s life strategies should be designed in such a way so that it minimises negative impact on the environment, the environment, which we are living in.
Дата добавления: 2016-07-18; просмотров: 2483;











