Language and Culture
It is estimated that Gaelic is spoken by some 70,000 people, many of whom live in the Hebrides (the islands off Scotland's west coast). The Scottish Executive provided 13.3 million to support Gaelic in 2001-02. Broadcasting is the largest single area, accounting for more than 8 million annually. In 2000-01 there were 1,862 children in Gaelic-medium education in 60 primary schools and 326 pupils in 14 secondary schools.
The annual Edinburgh Festival is one of the world's leading cultural occasions. Edinburgh Festivals bring about 120 million into the Scottish economy each year. The International Festival, Jazz Festival, Festival Fringe, Book Festival, Film Festival and Military Tattoo combine to make the Edinburgh Festival the largest arts event in the UK.
Economy
In the last 50 years the Scottish economy has moved away from the traditional industries of coal, steel and shipbuilding. Extraction of offshore oil and gas, growth in services and, more recently, developments in high-technology industries (such as chemicals, electronic engineering and information technology) have taken their place. Manufacturing still remains important, however, and Scotland's manufacturing exports in 2000 were valued at 18.3 billion.
The key features of the Scottish economy include:
Electronics. Scotland has one of the biggest concentrations of the electronics industry in Western Europe, employing about 40,000 workers. Electrical and instrumental engineering exports account for 56 per cent of Scotland's manufactured exports.
Oil and gas. Offshore oil and gas production has made a significant contribution to the Scottish economy in the last 30 years. Many of the UK's 115 offshore oilfields are at to the east of the Isles of Shetland and Orkney or off the east coast of the mainland.
Whisky. Whisky production continues to be important to Scotland. There are 90 distilleries in Scotland, most of them in the north-east.
Tourism is a major industry, supporting about 193,000 jobs. In 1999 tourists spent 2.5 billion in the country and there were around 12.4 million tourist trips including those originating in Scotland.
Financial services. A number of financial institutions are based in Scotland, including insurance companies, fund managers, unit trusts and investment trusts. There are four Scottish-based clearing banks, which have limited rights to issue their own banknotes.
Forestry. Scotland accounts for just under half of the UK's timber production. In the last ten years there has been significant international and local investment in wood-based panel production and in pulp and paper processing.
Fishing. Fishing remains significant, particularly in the north-east and in the Highlands and Islands. Today Scotland accounts for 70 per cent by weight and 60 per cent by value of the fish landed in the UK by British trawlers. Fish farming, particularly of salmon, has grown in importance. Today Scotland produces the largest amount of farmed salmon in the EU.
ENGLAND
ENGLAND is the largest of the four political divisions that make up the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales are the other three political divisions of the United Kingdom, which is often called Great Britain or simply Britain. England is the industrial and trading center of the United Kingdom.
England lies in the southern and eastern part of the island of Great Britain in the British Isles. It covers about three-fifths of the island. England has much charming countryside, with green pastures and neat hedges. But most of the English people live in sprawling cities. London, the capital, is England's largest city.
England has a rich history. The Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid industrialization, began there in the 1700's. English sailors, traders, explorers, and colonists helped found the British Empire--the largest empire in history. England produced William Shakespeare, who is considered the greatest dramatist of all time, and Sir Isaac Newton, one of history's most important scientists.
The English people have a long history of freedom and democracy. Their democratic ideas and practices have influenced many countries, including the United States and Canada. Most English people take great pride in their history and have deep respect for England's customs and traditions.
People
Population. England has a population of more than 53 million. About 95 percent of the people live in urban areas. About 35 percent live in the seven metropolitan areas.
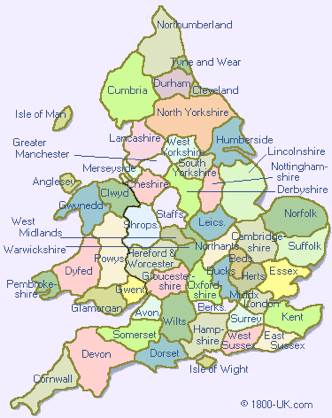
Greater London is the largest metropolitan area in England and one of the largest such areas in the world. It covers 610 square miles (1,580 square kilometers) and has about 6 1/2 million people. The six metropolitan counties, with the largest city of each in parentheses, are (1) Greater Manchester (Manchester), (2) Merseyside (Liverpool), (3) South Yorkshire (Sheffield), (4) Tyne and Wear (Newcastle upon Tyne), (5) West Midlands (Birmingham), and (6) West Yorkshire (Leeds).
| |
|
Until the mid-1800's, most of the English people lived in the countryside. During the Industrial Revolution, huge numbers of people moved to cities and towns to work in factories, mines, and mills. By the beginning of the 1900's, about four-fifths of the people lived in cities.
During the 1800's and early 1900's, millions of people left England to settle elsewhere. From the 1930's to the 1960's, the number of people moving to England outnumbered those leaving. Since the 1970's, however, the number leaving has been slightly larger than the number of people entering England. Most of the English emigrants have gone to the United States or to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, or other countries that were once part of the British Empire.
Refugees from Europe flowed into England before and after World War II (1939-1945). Since the 1950's, a large number of immigrants have come from Pakistan and from countries in Asia and the West Indies that belong to the Commonwealth. The Commonwealth is an association of countries and other political units that were once part of the British Empire. Most of the immigrants have settled in cities and towns already facing housing shortages. During the early 1960's, the British government began restricting immigration. The wives and children of immigrants already living in England make up about half of the new immigrants who are accepted each year.
Ancestry. Celtic-speaking people lived in what is now England by the mid-600's B.C. Over the next 1,700 years, the land was invaded by the Romans, Angles, Saxons, Jutes, Danes, and Normans. The Normans, the last people to invade England, came in A.D. 1066. Each group of invaders added its own traditions and speech to English civilization and helped shape the character of the English people.
Language. English is the official language of the United Kingdom. It developed mainly from the Anglo-Saxon and Norman-French languages. For a discussion of the English language, including the history of its development.
Many English words have different meanings in England than they have in the United States. In England, for example, freight cars are trucks and trucks are lorries. Gasoline is called petrol. Elevators are lifts, and cookies are called biscuits.
The way English is spoken varies throughout England. For example, people in the western part of England speak with a flatter accent and pronounce the letter r more clearly than do people in other areas. In east Yorkshire, in the northern part of England, the accent is soft and rather musical. People in the East End section of London speak a harsh dialect called cockney.
Way of Life
City Life. About 95 percent of the English people live in urban areas. The city centers are business and entertainment districts with modern buildings. They are crowded with shoppers, office workers, and people going to restaurants, theaters, and other places of relaxation and entertainment. On the edges of the cities lie suburban areas of well-kept brick houses with neat gardens. Gardening is a favorite hobby of the English. Most of the houses are detached (separate) or semidetached (two houses sharing a common wall).
Areas of substandard housing lie between the central business districts and the outer suburbs of many English cities, especially in northern England. Some of these areas consist of factories surrounded by blocks of terraced houses (identical houses in a row), which were built cheaply in the late 1800's. Many of the factories are abandoned or only partially used, and many of the houses are in poor condition. Some of the areas have apartment buildings called council flats that were built in the 1960's and 1970's by local authorities as public housing. Many of these buildings were built inexpensively, using poor construction methods, and have become run-down. Lack of housing and an increase in the number of homeless people are issues of concern in many cities in England. Other concerns in large urban areas include unemployment and problems resulting from the heavy use of automobiles, such as traffic congestion and air pollution.
Rural Life. Only about 5 percent of the English people live in rural areas. The rural areas of England, where farming is an important activity, include much of Devon and Cornwall in southwestern England; a broad strip of land in eastern England around a bay of the North Sea called The Wash; and the northern Pennines mountains. The people live in isolated rural dwellings or in country villages or towns.
Much of southeastern England and the areas surrounding England's northern and central cities appear rural. But the economies of these areas are actually extensions of cities. Most of the workers who live in these areas commute to jobs in the nearby cities. Area residents often visit the cities for shopping, dining, and entertainment.
Food and Drink. Traditional English cooking is simple. The English like roasted and grilled meats and use fewer spices and sauces than do other Europeans.
On Sunday, the midday meal, which is called dinner, traditionally consists of a joint (roast) of beef, pork, or lamb; roasted or boiled potatoes; a vegetable; and a sweet (dessert)--often fruit pie topped with hot custard sauce. Yorkshire pudding, a batter cake baked in meat fat, is often served with beef. Cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, peas, and carrots are common vegetables because they are easily grown in England's climate.
Other popular English dishes include roast chicken, steak and kidney pie, shepherd's pie, and bangers and mash. Steak and kidney pie is a stew made of beef and kidneys and topped by a pastry crust. Shepherd's pie is a casserole of ground meat and mashed potatoes. Bangers and mash are thick sausages served with mashed potatoes.
The English also like fish, especially cod, Dover sole, haddock, herring, and plaice. Fish and chips is a favorite dish for lunch, the late afternoon meal called tea, or supper. It consists of fried fish and French fried potatoes and is sold at specialty shops throughout England.
The favorite alcoholic drink in England is beer, which includes lager, ale, bitter, and stout. Many English people also like Scotch whisky. A popular nonalcoholic drink in England is squash, which is made by adding water to a concentrate of crushed oranges or lemons.
Recreation. Many English people, like people elsewhere, spend the evening watching television. Others visit their neighborhood pub (public house). The pub, or the local, as many people call it, is an important part of social life in England. At a pub, people may drink beer or other beverages, talk with friends, or play a game of darts or dominoes.
Many English people enjoy sports and outdoor activities, and they have many opportunities to participate in and watch organized sports. Others enjoy simply taking long hikes through the woods or countryside or working in their gardens.
England's most popular organized sport is football, the game Americans call soccer. During the football season, which lasts from August to May, about 20 million spectators watch the games. Millions of English people bet on the results of each week's football games by filling out pools coupons. The chances of winning are small, but winners have collected large amounts of money. At the end of the season, nearly 80,000 people jam Wembley Stadium in London to watch two teams battle for the Football Association Cup. International matches are held in England throughout the season.
Cricket has been popular in England for hundreds of years. It is played by two 11-member teams using a bat and ball. The English probably began playing cricket as early as the 1300's. Today, almost all towns and villages have cricket teams. Highlights of the cricket season are the international competitions called test matches between a team representing England and a team from Australia, India, New Zealand, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, or the West Indies.
Rugby football, which resembles American football, is played throughout England from late summer to late spring. People of all ages, but especially older people, enjoy bowls, a sport similar to bowling. There are thousands of bowls clubs in England. Other favorite sports include golf, horse racing, rowing, sailing, swimming, and tennis.
Hunting, horseback riding, fishing, and shooting are popular in the English countryside. Fox hunting is a traditional English sport in which hunters on horses follow a pack of hounds chasing a wild fox. Some wealthy people shoot game birds such as grouse, partridge, pheasant, snipe, and woodcock. Most game birds are found on private land.
The Arts. The English enjoy motion pictures, plays, and concerts. London is the center of English music and drama. But Birmingham and other major cities also have a growing number of music and theater companies.
England has a history of producing outstanding artists. It has been the birthplace of many noted architects, painters, and composers. But its greatest artists have probably been writers. Geoffrey Chaucer, Charles Dickens, William Shakespeare, and many other English authors wrote masterpieces of literature.
English architects have developed many different styles over the years. The Norman style began after the Norman Conquest of 1066. Buildings designed in the Norman style have heavy columns and semicircular arches. The Tudor style became popular for houses in the late 1500's, during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I. Tudor was the family name of the queen. Characteristics of the Tudor style include flat arches; many windows, gables, and chimneys; and timber frames filled in with brick and plaster.
During the 1600's, two of England's greatest architects were Inigo Jones and Sir Christopher Wren. Jones designed the Queen's House in Greenwich and remodeled St. Paul's Cathedral in London. Wren rebuilt St. Paul's and many other churches after they were destroyed by the Great Fire of London in 1666. Georgian architecture, which began during the 1700's, uses much brick and stone and has a simple, balanced design.
For hundreds of years, English painters followed the styles of other European artists. But during the 1700's, such painters as Thomas Gainsborough, William Hogarth, and Sir Joshua Reynolds began to develop their own individual styles. During the 1800's, John Constable and Joseph Turner produced beautiful landscapes. Important English painters of the 1900's include Duncan Grant, David Hockney, Paul Nash, Ben Nicholson, John Piper, and Graham Sutherland.
The English have always loved music, and many of their old folk songs are still sung throughout the English-speaking world. During the 1500's and early 1600's, such composers as Thomas Tallis and William Byrd wrote excellent church music. Henry Purcell, who lived in the late 1600's, is considered one of England's greatest classical composers. In the 1870's and 1880's, Sir William S. Gilbert and Sir Arthur Sullivan wrote many popular satirical operettas. Leading English composers of the 1900's include Benjamin Britten, Frederick Delius, Sir Edward Elgar, Gustav Holst, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Sir William Walton. Two English groups, the Beatles and the Rolling Stones, had enormous influence on the development of rock music.
English furniture makers were the best in Europe during the 1700's. Furniture collectors today prize the beautifully designed works of Thomas Chippendale, George Hepplewhite, and Thomas Sheraton. Also during the 1700's, Josiah Wedgwood and Josiah Spode produced lovely chinaware. Wedgwood and Spode pottery is still one of the United Kingdom's important exports.
WALES
WALES is one of the four major political divisions that make up the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. England, Northern Ireland, and Scotland are the other divisions of the United Kingdom, which is often called simply Great Britain or Britain. Cardiff is the capital and largest city of Wales.
Wales lies on the west coast of the island of Great Britain. It takes up about a tenth of the island. Wales has a wealth of scenic beauty. Its landscape includes low, broad mountains and deep, green valleys. Wales is bordered by extensions of the Atlantic Ocean on the north, west, and south, and by England on the east. Most of the Welsh people live in towns, cities, and industrial areas of southern Wales. The rest of Wales is mainly rural.
The Welsh take great pride in their heritage. Although Wales has been united with England for more than 400 years, the Welsh have kept alive their own language, literature, and traditions. The Welsh name for Wales is Cymru (pronounced KUM ree).
People
Population. Wales has a population of nearly 3 million people. Most live in the industrialized and formerly industrialized areas of southern Wales. The growth of population in these areas took place in the 1600's and during the Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid industrialization that began in the 1700's. At that time, people came to the region from rural Wales and from England. Cardiff, Newport, and Swansea grew as ports to serve the coal and iron industries.
Ancestry. Some Welsh are descended from prehistoric peoples from continental Europe who colonized Wales thousands of years ago. Many others trace their ancestry to such later settlers as the Celts, Romans, Anglo-Saxons, Vikings, Normans, and English.
Language. Wales has two official languages, Welsh and English. Either language may be used in the courts or for government business. Some newspapers are published partly or only in Welsh, and many radio and television programs are broadcast in both languages.
Welsh is still the daily language in many sections of western and northern Wales. In some parts of these areas, more than three-fourths of the people speak Welsh. Overall, however, the number of Welsh-speaking people has declined since 1901, when half the population spoke Welsh, to less than one-fifth today.
Welsh is one of the oldest languages in Europe. It is derived from ancient Celtic and has been influenced by each group of settlers. The letters j, k, q, v, x, and z are not used in modern Welsh. The letter y is always a vowel, and the letter w is usually used as one.
Certain letter combinations are considered part of the Welsh alphabet. They include the double letters dd, ff, and ll. The combination dd is pronounced like the th in they. The letter f sounds like the English v, and ff sounds like f. The ll sound is made by placing the tongue in the position for l and then trying to pronounce an h.
Way of Life
In general, the way of life in Wales is similar to that in the rest of the Western world. For example, many people relax in the evenings by watching television. In Wales, as in the United Kingdom as a whole, the pub (public house) is an important part of social life. A number of older customs also survive. On March 1, the feast of Saint David, the patron saint of Wales, people throughout the land wear the traditional Welsh symbols of the leek and daffodil.
City Life. About four-fifths of the Welsh people live in urban areas. Many urban dwellers live in large public housing developments on the outskirts of cities. These complexes were built in the 1950's and 1960's, and some of them have fallen into disrepair. Welsh metal-processing industries have declined since the 1950's, leading to increased unemployment in Welsh cities. Urban areas have also experienced a rise in crime, overcrowding, and other social problems.
In the steep-sided coal-mining valleys of southern Wales, many townspeople live in row houses. These houses have the same design and are attached in a row.
Rural Life. Approximately a fifth of the Welsh people live in rural areas. Welsh farms are small, and most are owned by the people who live on them. Many rural people live in stone cottages.
An older Welsh way of life has lasted in rural areas, especially where the Welsh language is the primary one. Ties to religion and to families tend to be stronger in these areas. However, many people fear that age-old customs may soon be lost. Rural housing has become scarce, and farming has become less profitable over the years. As a result, more and more young people have migrated to the cities to look for employment and housing. As the young people leave the countryside, they tend to abandon the old values and traditions.
Food and Drink. Most Welsh cooking is simple and uses local ingredients. Many Welsh people enjoy roast Welsh lamb served with mint sauce. Other favorite dishes include cawl, a clear broth with vegetables, and Welsh rarebit, which consists of melted cheese and butter served on toast. Laver bread is made from seaweed and oatmeal. Tasty Welsh cakes and cheeses are also popular. Beer is the traditional drink of Wales, and many pubs sell locally brewed beer. Ale is especially popular.
Recreation. Rugby football is the most popular sport in Wales. The Welsh rugby team competes internationally. Almost every town and village has its own team. Another popular sport is football, the game Americans call soccer. Cricket is also played widely in Wales.
In rural areas, many people fish, and some hunt foxes and wild duck. Snowdonia National Park and Brecon Beacons National Park have rugged terrain that is excellent for climbing and other mountain sports. Many people visit Pembrokeshire Coast National Park to hike along its coastal cliffs and admire its scenery.
The Arts. Wales is a land of poets and singers. The traditions of Welsh literature and music are among the oldest in Europe and date back more than 1,000 years to the bards (poet-singers) of the Middle Ages.
The most notable of early Welsh poets were Taliesin and Aneirin. Aneirin composed a poem called the Gododdin about the year 600. In it, he described the adventures of a band of noble warriors. Eleven Welsh stories written in the 1000's and known today as The Mabinogion rank among the most important works of medieval European literature. During the 1100's, Geoffrey of Monmouth composed poetry about the legendary King Arthur. Dafydd ap Gwilym, the greatest Welsh poet of the Middle Ages, wrote about love and nature during the 1300's.
The publication in 1588 of the complete translation of the Bible into Welsh ranks as one of the most important events in the history of Welsh literature. This Bible helped preserve the Welsh language and establish standards for written Welsh.
Many poets and other writers continued to use the Welsh language in the 1600's, 1700's, and 1800's, but other Welsh authors turned to English. Dylan Thomas, who wrote in English, became the most celebrated Welsh poet of the 1900's.
The eisteddfod (pronounced eye STEHTH vahd), a popular Welsh tradition, is a festival of poetry and music in which performers compete. Its origins date back to the Middle Ages, but the modern form began at the end of the 1700's. Annual eisteddfods, or eisteddfodau, are held throughout the land. The largest is the Royal National Eisteddfod. It is held in various cities and towns, alternately between northern and southern Wales.
Wales has a rich tradition of choral music that developed in the 1700's at a time of religious revival. The Welsh National Opera has also become world famous.
NORTHERN IRELAND
NORTHERN IRELAND is the smallest of the four major political divisions that make up the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. England, Scotland, and Wales are the other divisions of the United Kingdom, which is often simply called Great Britain or Britain. Belfast is Northern Ireland's capital and largest city.
Northern Ireland occupies the northeastern corner of the island of Ireland. It takes up about a sixth of the island. The independent Republic of Ireland occupies the rest of the island. Northern Ireland is often called Ulster. Ulster was the name of a large province of Ireland until 1920, when Northern Ireland was separated from the rest of Ireland.
Religion has long divided the people of Northern Ireland into rival political, social, and cultural groups. The majority of Northern Ireland's people are Protestants, and they have traditional ties to the rest of the United Kingdom. Nearly all the rest of the inhabitants are Roman Catholics, as are most of the people in the Republic of Ireland to the south. In general, Protestants want Northern Ireland to remain in the United Kingdom, and Catholics want it to become part of the Irish Republic. The continuing dispute between the two groups has sometimes led to riots, bombings, and other outbreaks of violence and terrorism, often called the troubles.
People
Population. More than 1 1/2 million people live in Northern Ireland. About two-thirds of them live in urban areas. The largest cities are Belfast and Londonderry.
Ancestry. A majority of the people who live in Northern Ireland are descended from English and Scottish settlers who arrived there since the 1600's. Most of the rest trace their ancestry to the earlier Celtic, Viking, and Norman settlers of the island of Ireland.
Language. English is the official language of Northern Ireland, and all the people there speak it. The Irish language, a form of Gaelic once used throughout Ireland, is taught to children in Roman Catholic schools and in some Protestant schools.
Way of Life
Most people in Northern Ireland have a way of life similar to that of people in the rest of the United Kingdom. Many people in Northern Ireland relax in the evening by watching television. Motion pictures are also popular. As in the rest of the United Kingdom, pubs (public houses) are an important part of the social lives of many people in Northern Ireland. People gather in pubs to drink beer and other beverages, eat sandwiches, talk with friends, and listen to music.
Many Protestant men belong to an organization called the Orange Order and are known as Orangemen. The Orangemen hold parades every July 12. The parades celebrate the victory of King William III, a Protestant, over King James II, a Roman Catholic, in the Battle of the Boyne in 1690. The "Twelfth" is a public holiday in Northern Ireland. A similar association of Roman Catholics, the Ancient Order of Hibernians, holds parades on August 15 and sometimes on March 17. August 15 is the Roman Catholic Feast of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary. March 17 is St. Patrick's Day. Saint Patrick is the patron saint of Ireland.
City Life and Rural Life. More than half the people of Northern Ireland live in or near the cities of Belfast and Londonderry, which is also called Derry. Bloody rioting and numerous acts of terrorism have disrupted life in Belfast and Londonderry since the 1960's. However, British government aid has helped make the cities modern--and more peaceful--urban centers. In Belfast, for example, new hotels, offices, and shopping malls have been built, and extensive home-building projects have eased the worst of the city's housing problems.
About a third of the people of Northern Ireland live in rural areas. Most of these people earn their living by farming.
Food and Drink. The people of Northern Ireland enjoy simple meals of meat, potatoes, vegetables, and bread. They also eat large amounts of poultry, eggs, dairy products, and fish. Tea is the most popular drink in Northern Ireland. A favorite alcoholic beverage is beer.
Recreation. Northern Ireland's most popular organized sport is football, the game that Americans call soccer. Other popular sports in Northern Ireland include cricket, which is played with a bat and a ball; Gaelic football, which resembles soccer; handball; hurling and camogie, which are somewhat similar to field hockey; and rugby, a form of football. Many people in Northern Ireland enjoy boating, fishing, golf, and swimming.
The Arts. The most famous cultural event in Northern Ireland is the international arts festival hosted each November by the Queen's University of Belfast. This festival features musical performances, dramatic productions, art exhibits, motion pictures, lectures, and other events.
The Ulster Orchestra and Opera Northern Ireland, both of which perform in Belfast, are well known. In addition, several individuals from Northern Ireland have established international reputations in music. They include the flutist James Galway and the pianist Barry Douglas.
Northern Ireland is also known for talented writers. The poetry of Seamus Heaney and John Hewitt, the novels of Brian Moore, and the plays of Brian Friel have attracted many readers.
Дата добавления: 2016-07-18; просмотров: 2170;











