Structural and parametrical identification.
Identification is called finding of the Am model optimum somewhat (or estimates F of the operator) an object the being function of entrance (U) and days off (Y or X) parameters of the system constructed by results of observations over entrance and output variables of an object.
The received model, (in case of its adequacy to the researched object) is generally intended for replacement of a real object in tasks of control, the forecast, designing, search of the optimum modes and conditions, imitation of the phenomena and devices, etc.
Task of identification is called the return task of system synthesis. 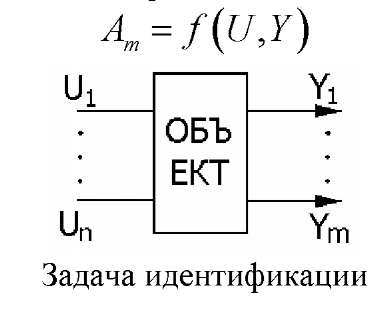
Figure 10.2.Problem of identification
Distinguish two types (problem) from problems of identification:
1. structural identification (in the broadest sense);
2. parametrical identification (identification in the narrow sense of the word).
Structural identification means creation of " model a black box", i.e. information on an object is absent in whole or in part. The main task of structural identification - definition of structure of model (see the figure 10.5).

Figure 10.5. Structural identification
The first problem - structural identification is, in essence, the main problem of all process of the modeling consisting of the following four main stages:
• problem definition
• choice of structure of model and mathematical description of her blocks;
• model research;
• experimental check of model.
Structure of model yet not model, and for determination of her parameters it is necessary to have measurements. The problem of determination of parameters of model of observations of work of an object at the set structure of model is called identification in narrow sense or parametrical identification. For example, the system of the equations describing some object is known. It is necessary to define only coefficients of the equations. The procedure of structural identification is shown in the figure 10.6
identifications - definition of structure of model (see the figure 10.5).
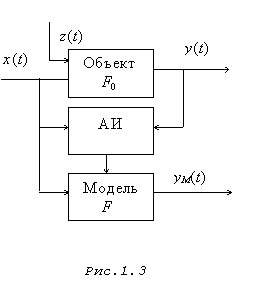
AI – an identification algorithm
Figure 10.6. Procedure of identification
The second problem (parametrical identification) at the set structure of model gives in to formalization and is closed with the fourth stage modeling.
Thus, in relation to multi-stage process of modeling in general identification acts as the instrument of check of hypotheses of compliance of structure or parameters of an object and model on the basis of experimental data about his functioning. Character and degree of discrepancy are used at the same time for adoption of the substantial or formalized decisions on correction of model (see figures 10.7 and 10.8)
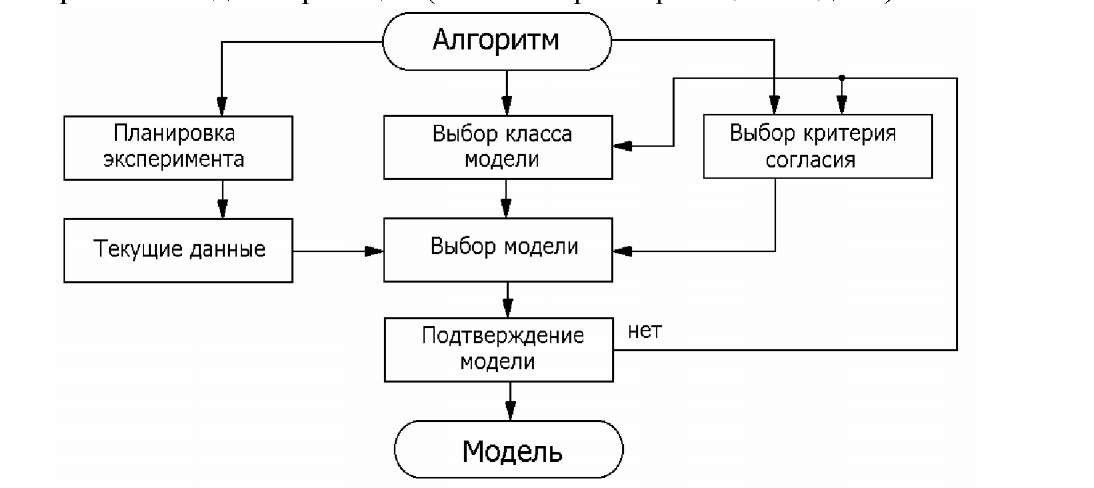
Figure 10.7. General scheme of identification of model
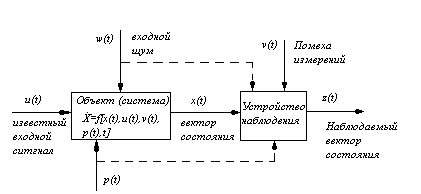
Figure 10.8. Block diagram of identification of model
Planning methods of an experiment allow to organize an experiment effectively. The choice of a class of model and model – rather difficult procedure in case of the solution of which usually it is necessary to make the compromise choice between complexity of model and its accuracy. The choice of criterion of a consent are the choice of criterion of accuracy of the mathematical description. Often use for this purpose a method of the smallest squares. The method of the smallest squares doesn't require any aprioristic information. In separate practical tasks of automatic control as measures of comparison it is possible to accept various characteristics (temporary, frequency, etc.) object and model. Criterion of identification in this case is the mismatch of these characteristics. However, if the model is used in the self-adjusted SAU, setup of model on dynamic characteristics requires availability of measuring instruments of dynamic characteristics of an object and model that leads to constructive complication of SAU and reduction of speed of contours of self-adjustment.
Thus, the task of identification is formulated as follows: by results of observations of entrance and output variables of an object to construct its model optimum somewhat. At the same time an object is in the normal mode of functioning (i.e. in the conditions of accidental indignations and hindrances). In other words, if an object is described by some unknown operator F0, then having the measured values of an entrance and an exit it is necessary to construct Estimate, the operator of an object, optimum that is some criterion.
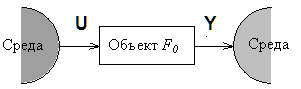
Figure 10.9. Interaction of an identifiable object with Wednesday
The figure 10.9 illustrates interaction of an identifiable object with Wednesday. This interaction happens on U and Y channels. On channel U – an entrance Wednesday influences an object, and on channel Y (exit) an object influences on Wednesday. The task of identification comes down to determination of the operator of model connecting an entrance and an exit of an object Y = F(U).
As often there is no model of the environment influencing an object, it is natural to consider its entrance as stochastic function of time which statistical properties are generally unknown. However observations of an entrance and an exit of an object, i.e. implementation of the U and Y functions are known. Can influence an object not observed factors of V (t) which are considered as accidental hindrances.
Thus, identification is a synthesis of some criterion of a consent (accuracy) of the model operator optimum that is of the researched object with use of results of observations of its entrance and output variables.
Classification of methods of identification. According to the modern theory it is possible to offer the following classification of identification:
1) on a resulting effect of identification (structural and parametrical);
2) on a method of studying of an object of identification (active and passive)
3) as identifiable model (linear and nonlinear; determined and stochastic; with continuous and discrete time; stationary and non-stationary; one-dimensional and multidimensional; static and dynamic; with the concentrated and distributed parameters).
Active and passive identification. In case of an active method of identification implementation of an entrance is created by the researcher by giving on an entrance of an object of a test signal of a desirable form (a spasmodic signal, a pulse signal, a signal in the form of harmonic, rectangular, trapezoidal, triangular oscillations, etc.). Implementation of an exit of an object is its reaction to a test signal. At the same time in the modern theory of identification methods of optimum planning of an experiment are widely applied. In case of a passive method of identification as implementations of an entrance and exit of an object accept their natural changes in process of normal functioning of an object.
Ha the drawing 10.10 is shown communication between aprioristic information (about structure) and a posteriori information on measurements) in case of creation of model. The upper part of the drawing illustrates process of creation of model as a specific example of use of physical laws with the subsequent linearization and transformation to system of the ordinary differential equations. I received the equations determine structure of model. Ha every step arise errors. B of the lower part of the drawing is illustrated the procedure of estimation based on measurements and including data processing and algorithm of estimation. Here too it is necessary to consider different types of errors.
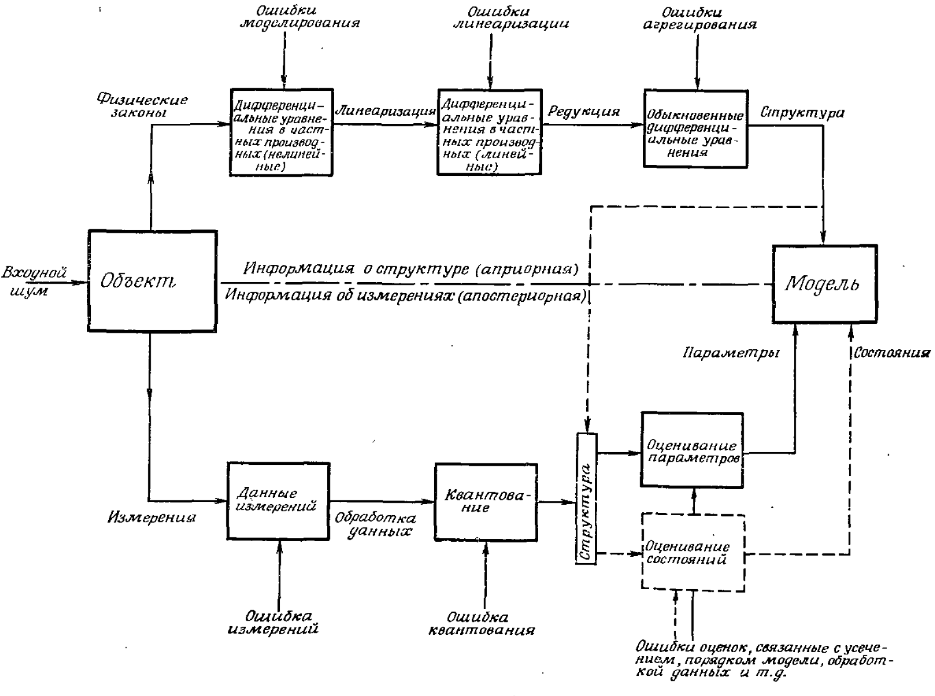
Figure 10.10. Communication between aprioristic information (about structure) and a posteriori information on measurements)
Test questions
1. Give the main stages of identification.
2. A concept about aprioristic and a posteriori information.
3. Criteria and indicators of identification quality.
4. Classification of identification methods.
5. Principles structural and parametrical identification.
6. Principles of active and passive identification.
Basic Literature
1. Гроп Д. Методы идентификации систем. - М.: Мир, 1979
2. Эйкхофф П. Основа идентификации систем управления. - М.: Мир, 1975.
Дата добавления: 2017-05-02; просмотров: 1146;











