Various methods of streaking
Pour Plate Method
This method involves plating of diluted samples mixed with melted agar medium. The main principle is to dilute the inoculum in successive tubes containing liquefied agar medium so as to permit a thorough distribution of bacterial cells within the medium. Here, the mixed culture of bacteria is diluted directly in tubes containing melted agar medium maintained in the liquid state at a temperature of 42-45°C (agar solidifies below 42°C).
The bacteria and the melted medium are mixed well. The contents of each tube are poured into separate Petri plates, allowed to solidify, and then incubated. When bacterial colonies develop, one finds that isolated colonies develop both within the agar medium (subsurface colonies) and on the medium (surface colonies). These isolated colonies are then picked up by inoculation loop and streaked onto another Petri plate to insure purity.
Pour plate method has certain disadvantages as follows: (i) the picking up of subsurface colonies needs digging them out of the agar medium thus interfering with other colonies, and (ii the microbes being isolated must be able to withstand temporary exposure to the 42-45° temperature of the liquid agar medium; therefore this technique proves unsuitable for the isolation of psychrophilic microorganisms.
However, the pour plate method, in addition to its use in isolating pure cultures, is also used for determining the number of viable bacterial cells present in a culture.
Figure 6. Pour plate method
Spread Plate Method
In this method the mixed culture of microorganisms is not diluted in the melted agar medium (unlike the pour plate method); it is rather diluted in a series of tubes containing sterile liquid, usually, water or physiological saline. A drop of so diluted liquid from each tube is placed on the centre of an agar plate and spread evenly over the surface by means of a sterilized bent-glass-rod.
The medium is now incubated. When the colonies develop on the agar medium plates, it is found that there are some plates in which well-isolated colonies grow. This happens as a result of separation of individual microorganisms by spreading over the drop of diluted liquid on the medium of the plate.
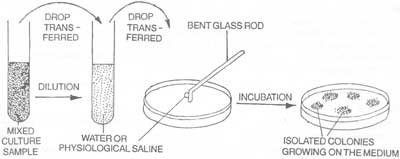
Figure 7. Spread plate method
Control questions:
1. Isolation of accumulative culture from pure cultures?
2. Principles of spread plate method?
3. Principles of pour plate method?
4. Principles of streak plate method?
Дата добавления: 2021-02-19; просмотров: 711;











