What is the skeleton? What does it do?
The skeleton is the entire collection of bones, cartilages, joints, tendons and ligaments inside our body.
Bone is a type of tissue that contains collagen and calcium phosphate, a mineral crystal. Bones provide support and protection for body organs.
Cartilage is a form of tissue that contains chondrin. Cartilage provides flexible support for certain structures in adult humans including the nose, trachea, and ears.
Tendon is a fibrous band of connective tissue that is bonded to bone and connects bone to bone.
Ligament is a fibrous band of connective tissue that joins bones and other connective tissues together at joints.
Joint is a site where two or more bones or other skeletal components are joined together.
The skeletal system is one of the major systems of the human body, and has four major functions:
• It protects vital organs, such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
• It supports the body and gives us our distinctive shape. Without our skeleton, we would look more like a slug.
• It allows us to move in particular ways.
• It makes new blood cells to maintain a healthy bloodstream.
With so many important jobs to do, the skeleton is a vital part of the human body.
The skeletal system in an adult body is made up of 206 individual bones. The bones form the skeleton of the body. The bones which form the skeleton or bony framework of the body include the bones of the head and the face, the bones of the trunk, the bones of the lower and upper limbs.
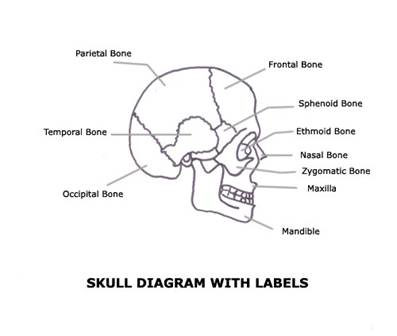 The bones of the head and the face:
The bones of the head and the face:
At the upper end of the backbone there is the skull (cranium). Inside the skull is the brain. The bones of the head include the bones which make up the box-like structure, the skull, and freely movable bone which forms our lower jaw. Our face is made up of 14 bones. The most important boned of the face are mandible (lower jawbone) and maxilla (the upper jawbone).
The bones of the trunk:
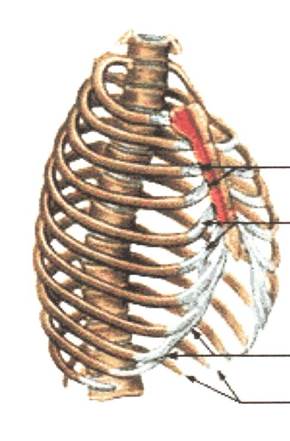 The most important part of the skeleton is the backbone (spinal cord,vertebral column) . It is so important that naturalists divided all animals into two classes - those which have a backbone and those which have none. All the higher animals have a backbone, or vertebral column and they are therefore called (называются) vertebrate animals. The others are called invertebrate animals. The vertebral column, or the spinal column, is made up of 24 small bones, each of which is known as a vertebra.
The most important part of the skeleton is the backbone (spinal cord,vertebral column) . It is so important that naturalists divided all animals into two classes - those which have a backbone and those which have none. All the higher animals have a backbone, or vertebral column and they are therefore called (называются) vertebrate animals. The others are called invertebrate animals. The vertebral column, or the spinal column, is made up of 24 small bones, each of which is known as a vertebra.
There is another box of bones in front of the backbone. The ribs, which join the backbone behind and bend round towards the breastbone in front, form a strong cage — the chest.
The shoulder is made of two bones that together allow the attachment of the arm to the body. The bones of the shoulder are Scapula and Clavicle. The scapula is a flat, triangular bone that connects the humerus (upper arm) with the clavicle. The clavicle is a pair of small long bones that join the scapula to the sternum. The clavicle is the only long bone that lies horizontally.
The bones of the lower and upper limbs:
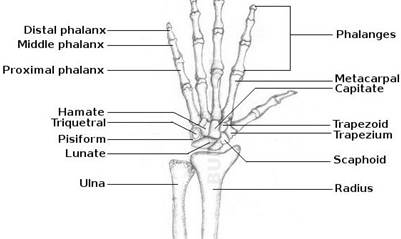 The bones of the hands can be divided into those that make up the upper arm, the lower arm, the wrist, the palm and the fingers.
The bones of the hands can be divided into those that make up the upper arm, the lower arm, the wrist, the palm and the fingers.
Between the shouldet and the elbow there is only one bone (humerus).
The Humerusis a single long bone of the upper arm. It runs from the shoulder to the elbow. The humerus connects the scapula to the bones of the forearm.
Between the elbow and the wrist there are two bones (radius and ulna).
The Radius is one of the long bones of the forearm. It starts from the elbow and continues to the wrist.
The Ulna is a long bone that runs parallel to the radius, along the forearm.
In the wrist there are eight small bones. They are bound (связаны) together, but their large number allows the wrist to bend freely. The Carpal Bones are the bones of the wrist.
In the bones of the hand there are five long bones — one for each finger and one for the thumb. Each of the fingers has three bones, and the thumb has two. Thus we have twenty-seven bones in the framework of the hand and wrist alone. The Metacarpal Bones are the bones of the palm. Phalanges are the bones of the fingers.
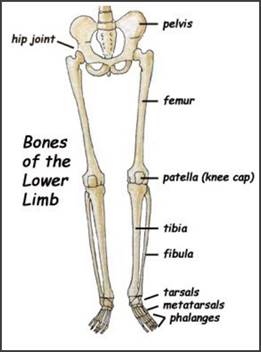 The bones of the legs are those that make up the thigh, the lower half of the legs, and the feet.
The bones of the legs are those that make up the thigh, the lower half of the legs, and the feet.
The Pelvis is a bone attaches to the spinal cord that joints the femur and the trunk.
Between the pelvis and the knee cap (patella) there is only one bone (femur).
The Femur is the longest bone in the human body, and is also known as the thigh bone.
Between the patella and the ankle there are two bones (tibia and fibula).
The tibia is the second longest bone in the human body. Along with the fibula, it forms the lower part of the leg below the knee. The tibia is considered to be the strongest bone of the body. It is commonly known as the shin bone.
The fibula is a long but thin bone which, along with the tibia, forms the lower part of the human leg. It is attached to the tibia at both the ends. The fibula is also known as the calf bone.
The patella is a triangular bone that forms a protective cap over the knee joint. Also known as the kneecap. It is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body.
The tarsal bonesare the bones of the ankle, and there are 14 tarsal bones, 7 on each foot.
There are 5 metatarsal bones in each foot, one corresponding to each digit. These lie between the tarsal bones and the phalanges.
The Phalanges are bones of the toes of the feet. There are 5 phalanges in each foot.
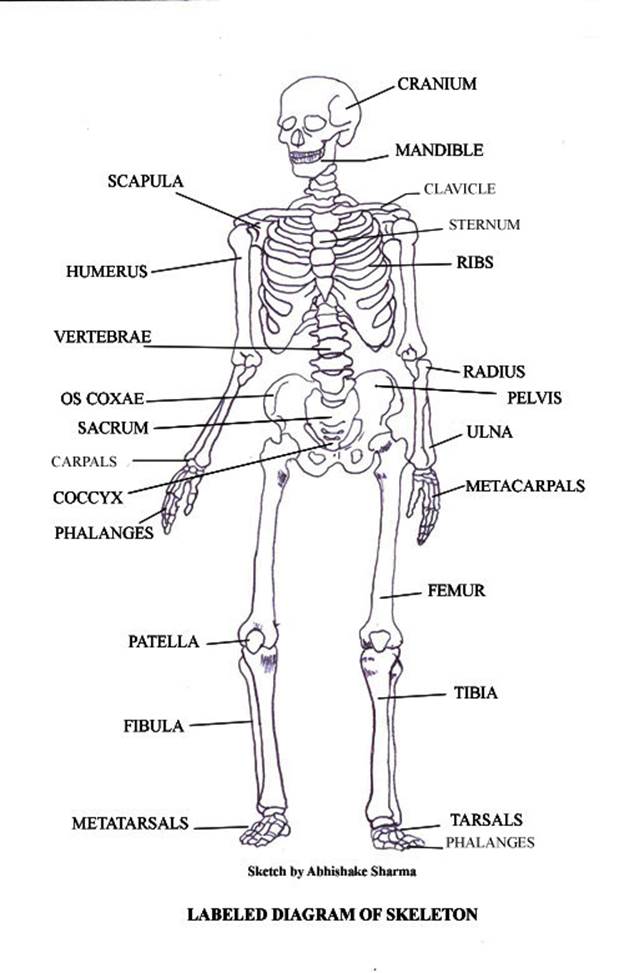
MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Muscular system is the system of Human Body that provides motor power for all movements of body parts. Muscular system is composed of special tissue called muscular tissue. Muscles have the ability to contract actively to provide the force for movements of body parts. Muscular system is an important system of human body because without it, life will completely stop. Muscles produce not only those movements that are under the control of our will and that we can see and feel, but also those movements that are responsible for activities like breathing, digestion of food, pumping of blood etc. Their function is to produce force and cause motion.
Functionally we divide all muscles into two groups: voluntary and involuntary muscles.
Muscle is a contractile tissue (сокращающаяся ткань) and is derived from the mesodermal layer (мезодермальный слой) of embryonic cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments (нити) that move past each other and change the size of the cell.
There are three types of muscle tissue. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth (гладкие) muscles.
 Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" (произвольно сокращающаяся мышца) form most of the human body weight. They are under the control of human will and all body movements occurring by our will are produced by skeletal muscles. They are called skeletal muscles because they are almost always found attached to the skeleton and produce movements in different parts of the skeleton. An average adult male is made up of 42% of skeletal muscle and an average adult female is made up of 36%.
Skeletal muscle or "voluntary muscle" (произвольно сокращающаяся мышца) form most of the human body weight. They are under the control of human will and all body movements occurring by our will are produced by skeletal muscles. They are called skeletal muscles because they are almost always found attached to the skeleton and produce movements in different parts of the skeleton. An average adult male is made up of 42% of skeletal muscle and an average adult female is made up of 36%.
Smooth muscle or "involuntary muscle" form the soft body organs like stomach, intestine, blood vessels uterus, urethra, bladder etc. They are not under the will of human beings and are responsible for unconscious body activities like digestion of food. They are called smooth muscles because when seen under the microscope, they do not have any striation in contrast to the other two types of muscles. 
 Cardiac muscle is also an "involuntary muscle" and is found only in the human heart. They are extremely strong and powerful muscles. They are not under the control of human will. The pumping of blood by human heart is because of the force provided by the contraction of cardiac muscles.
Cardiac muscle is also an "involuntary muscle" and is found only in the human heart. They are extremely strong and powerful muscles. They are not under the control of human will. The pumping of blood by human heart is because of the force provided by the contraction of cardiac muscles.
Muscular system has the following important functions in human body;
1. MOVEMENTS OF BODY PARTS: Skeletal muscles are responsible for all voluntary movements of human body parts. They provide the force by contracting actively. In other words, muscles are motors of body where chemical energy of food is converted into mechanical work.
2. STABILITY AND POSTURE: Skeletal muscles stabilize human skeleton and give a proper posture to human beings. Some joints of human body are weak and they require the support of muscular system to achieve stability. Skeletal muscles are very important for such joints.
3. HEAT PRODUCTION: A large share of body’s energy is used by muscular system. As a result of high metabolic rate, muscles produce great amount of heat in the body. Heat produced by muscles is very important in cold climates.
4. CIRCULATION: Cardiac muscles provide the main force for circulation of blood throughout human body. The regular pumping of heat keeps the blood in motion and nutrients are readily available to every tissue of human body.
5. HELP IN DIGESTION: Smooth muscles of organs like stomach and intestine help the digestive system in the process of digestion of food.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Nervous systemis the chief controlling and coordinating system of the body. It controls and regulates all voluntary and involuntary activities of human body. There are three characteristic properties of nervous system of human body;Sensitivity, Conductivity and Responsiveness. The structural and functional unit (элемент) of nervous system is called neuron.
Parts of nervous system:
Nervous system of human body is divided into two parts: Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Central nervous systemincludes brain and spinal cord.
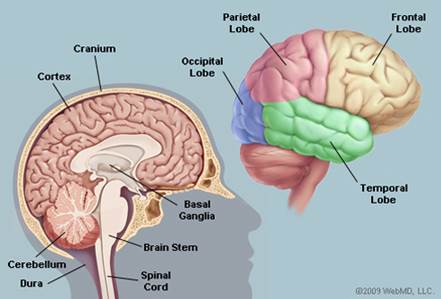 The brain
The brain
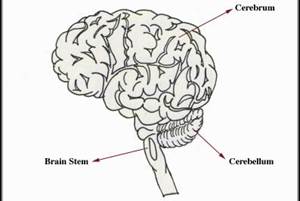
The brain lies within the skull and is shaped like a mushroom. The brain consists of four principal parts:
the brain stem
the cerebrum
the cerebellum
the diencephalon
The brain weighs approximately 1.3 to 1.4 kg. It has nerve cells called the neurons and supporting cells called the glia.
 There are two types of matter in the brain: grey matter and white matter. Grey matter receives and stores impulses. Cell bodies of neurons and neuroglia (нейроглия) are in the grey matter. White matter in the brain carries impulses to and from grey matter. It consists of the nerve fibers (axons).
There are two types of matter in the brain: grey matter and white matter. Grey matter receives and stores impulses. Cell bodies of neurons and neuroglia (нейроглия) are in the grey matter. White matter in the brain carries impulses to and from grey matter. It consists of the nerve fibers (axons).
The brain stemis also known as the Medulla oblongata. It is located between the pons and the spinal cord and is only about one inch long.
The cerebrumforms the bulk (основная масса) of the brain and is supported on the brain stem. The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres. Each hemisphere controls the activities of the side of the body opposite that hemisphere. The hemispheres are further divided into four lobes:Frontal lobe, Temporal lobe, Parietal lobe, Occipital lobe.
The cerebellumis located behind and below the cerebrum.
The diencephalon includes the thalamus and hypothalamus. The thalamus is where sensory and other impulses go and coalesce (соединяться). The hypothalamus is a smaller part of the diencephalon.
The spinal cordis a long tube like structure which extends from the brain. The spinal cord is composed of a series of 31 segments. Both motor and sensory nerves are located in the spinal cord. The spinal cord is about 43 cm long in adult women and 45 cm long in adult men and weighs about 35-40 grams.
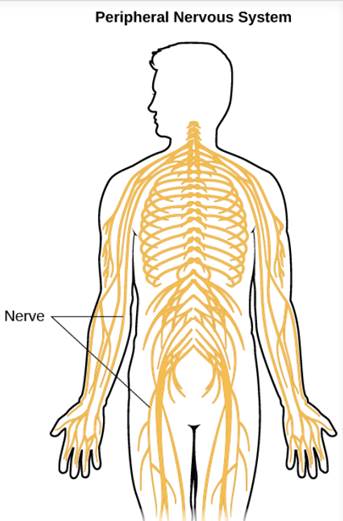 Peripheral nervous system includes all the parts of nervous system except brain and spinal cord. It is further divided into two components: Somatic nervous system and Autonomic nervous system. The Somatic Nervous System is the part of the peripheral nervous system that handles (осуществлять) voluntary control of body movements. It contains all the neurons connected with skeletal muscles and skin.
Peripheral nervous system includes all the parts of nervous system except brain and spinal cord. It is further divided into two components: Somatic nervous system and Autonomic nervous system. The Somatic Nervous System is the part of the peripheral nervous system that handles (осуществлять) voluntary control of body movements. It contains all the neurons connected with skeletal muscles and skin.
The Autonomic Nervous System is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as an involuntary control system (below the level of consciousness), and controls visceral (висцеральный) functions.
Nerves:
Nerves are solid cords composed of bundles (узел) of nerve fibers (нервное волокно) (each nerve fiber is an axon with its coverings) bound together by connective tissue. Nerves are of two types: Spinal nerves and Cranial Nerves.
Spinal Nerves: Spinal nerves arise(брать начало) from the spinal cord. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves in human body.
Cranial NervesCranial nerves arise from the brain. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in human body
Functions of nervous system:
1. CONTROL OF ALL BODY FUNCTIONS: Nervous system is the master system of human body. It controls the activity of all other systems in such a way that all the systems collectively make a human being.
2. COORDINATION OF DIFFERENT BODY ORGANS: Nervous system not only produces coordination between different systems, but also between different organs of a system. So nervous system is not only important for formation of an organism by different organ systems, but also for formation of a system by different organs of human body.
Дата добавления: 2017-01-26; просмотров: 3905;











