Political map of the USA
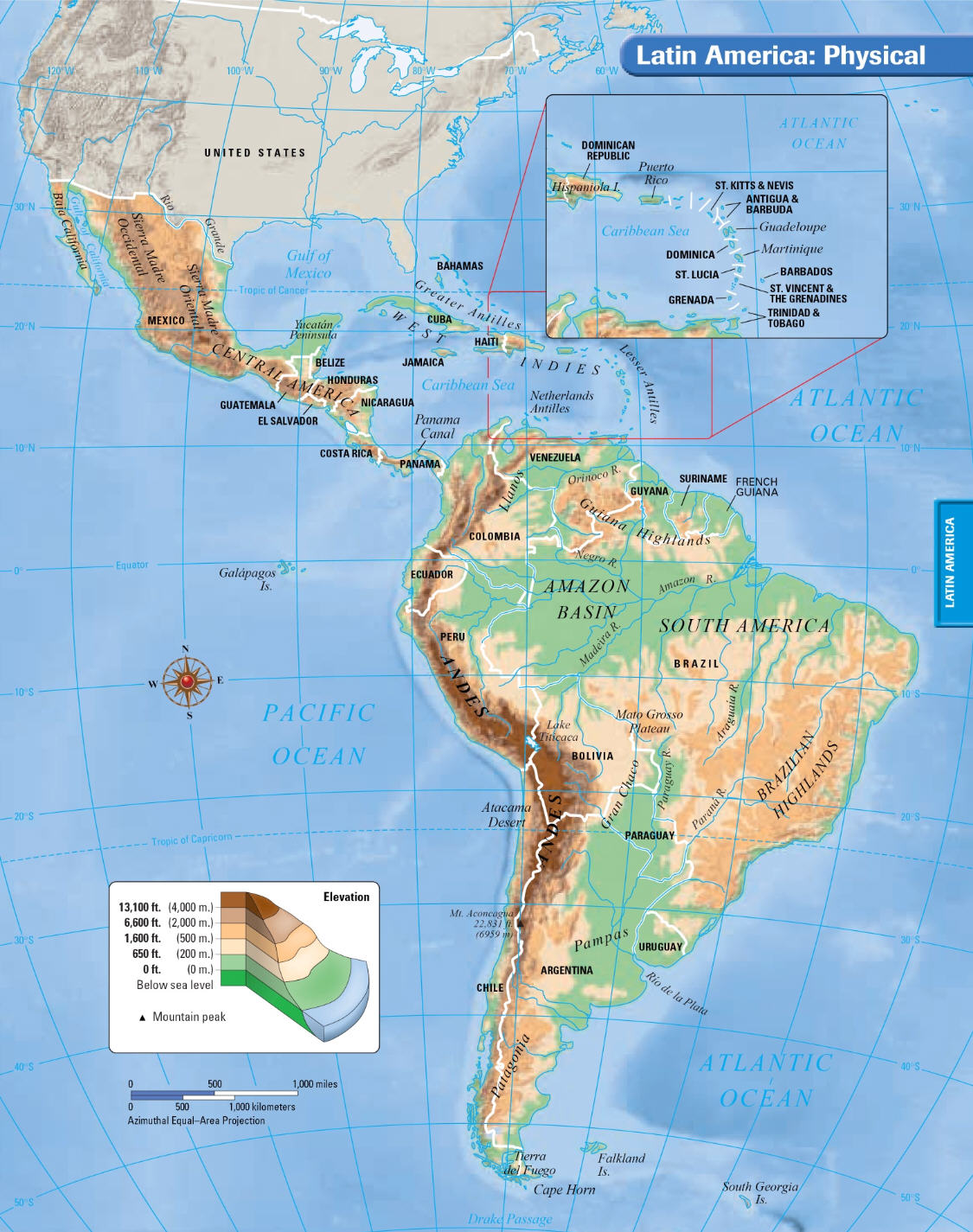
Latin America. General characteristic.
Plan:
1. Topography
2. Climate
3. Resources
Topography
Some facts:
ü 19,1 million square km
ü 12,6% of the earth’s surface
ü Historical roots: Spain and Portugal
ü Spanish and Portuguese based on Latin: Latin America
ü Population – about 590 million
Regions of Latin America:
1. Middle America
a. Mexico
b. Central America
2. Caribbean
• a. Bahamas:
• b. Greater Antilles (Cuba, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic)
• c. Lesser Antilles
3. South America (Venezuela (Caracas), Colombia (Bogota), Ecuador (Quito), Peru (Lima), Bolivia (La Paz), Chile (Santiago), Argentina (Buenos Aires), Uruguay (Montevideo), Paraguay (Asuncion), Brazil (Brasilia), Guyana (Georgetown), Suriname (Paramaribo), French Guiana (Cayenne)
Bodies of water: Latin America is washed by the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean in the east and the Pacific Ocean in the west; Amazon Basin is the largest river system in world by volume; second in length; Gulf of Mexico – the main place to extract oil, Lake Titicaca - World’s highest lake (3812 m above sea level, depth - 304m., the largest fresh water basin, 8290 sq. km)
Mountains and peaks: The Andes
ü Relatively young, 5,000 miles long;
ü Contain valuable metals and minerals
The Uplands of Mexico and Central America
ü Most major cities and population found here
ü Rich volcanic soils
The Shields
ü Large upland plateaus of exposed crystalline rock
ü Brazilian shield is the largest, covering most of Brazil
ü Has natural resources and settlement
Mato Grosso -a high plateau region in southwestern Brazil that forms a watershed between the Amazon and Plate river systems
The Llanos- an extensive grassy treeless plain in South America
The Pampas -large treeless plains in South America
Climate
Dry climate
The Atacama is one of the driest places on Earth. In some parts no rain has fallen for 400 years.
Tropical climate
In some tropical climates there are warm temperatures and plenty of rainfall all year. This creates rainforests. Rainforests are found in the Amazon Basin, some Caribbean islands and parts of Central America.
Other areas in Latin America are wet and dry and warm all year. For example, lowlands of Mexico, western Central America and southern Brazil.
Temperate climate
In temperate climates, warm seasons alternate with cool seasons. Temperate climates are good area for grazing for livestock and farming. Some areas where there are temperate climates are in Paraguay, Uruguay and northern Argentina.
In Latin America the chief influence on climate is elevation above sea level. Climate can vary greatly depending on if you are in the lowlands or highlands. Latin Americans have their own terms for the changes in climate: tierra caliente, tierra templada and, tierra fria.
Resources
Two very important cash crops are coffee and cacao, which is the source of cocoa, the base ingredient in chocolate. Brazil is the world’s largest exporter of coffee, and it used to be one of the largest exporters of cacao. South America’s temperate climates are home to a number of industrial crops and livestock. Corn is produced throughout the temperate climates, and soybeans have become an increasingly lucrative crop in the Pampas.
The Pampas’ vast, high-quality pastures are also the center of South America’s huge ranching industry. Brazil is the world’s third-largest beef exporter (behind only Australia and the United States). Argentina is also an important beef exporter.
Forestry is the management of trees and other vegetation in forests. It is a major economic activity for tropical South America, especially the Amazon River basin. Marine fisheries are the most important economic activity along South America’s Pacific coast.
The mining industry is one of South America’s most important economic engines. The continent contains about one-fifth of the world’s iron ore reserves. Iron and steel (an iron product) are used in construction and machinery throughout the world.
More than one-quarter of the world’s known copper reserves are in South America, mostly in Peru and Chile.
Other important metal deposits include tin, used to solder metallic surfaces; lead, used in construction, batteries, and bullets; and zinc, used as an anti-corrosion agent. Brazil, Peru, and Bolivia are major producers of tin. Lead and zinc deposits are found primarily in higher elevations of Peru, Bolivia, southern Brazil, and northern Argentina.
South America is home to some deposits of oil and natural gas, which are drilled for energy and fuel. Oil and gas extraction is the dominant industry of Venezuela, with major deposits found around Lake Maracaibo and the El Tigre region. The oil sector accounts for about one-third of Venezuela’s total gross domestic product (GDP).
Дата добавления: 2021-10-28; просмотров: 553;











